- Science
Imec and Sarcura introduce scalable on-chip detection of human white blood cells
On-chip flow cytometer using integrated photonics paves the way for high-throughput cell analysis
Imec, a world-leading research and innovation hub in nanoelectronics and digital technologies, and Sarcura GmbH, an Austrian early-stage technology start-up, present their proof-of-concept on-chip flow cytometer using integrated photonics. Published on 20th May 2024 in Scientific Reports, part of the Nature Publishing Group, this innovation offers a unique platform for the detection and discrimination of human leukocytes and marks a significant stride towards cost-effective, scalable, and highly parallelized cell analysis.
Accurate identification of human cells is a key operation in modern medicine, pivotal for understanding disease mechanisms and advancing targeted and personalized treatments. With the advent of cell manufacturing, living cells can now be engineered to function as treatments, notably in groundbreaking therapies like CAR-T immune cell therapy for cancer. The ability to identify these therapeutic cells in complex cell products at high throughput is crucial, and often time sensitive.
The method of choice today is flow cytometry, which enables characterization of cell populations based on the physical and chemical characteristics of individual cells as they flow past a laser. However, the current implementation include bulky instrumentation, complex and manual workflows (posing contamination risks), and high operational costs. These challenges hinder widespread availability and adoption of cell therapies in decentralized settings.
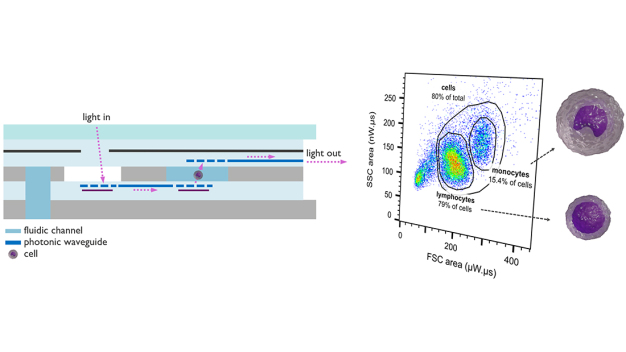
To address these limitations, imec harnesses its expertise in CMOS technology, photonics, and fluidics to automate, miniaturize and parallelize flow cytometry. In a study published in Scientific Reports imec, together with Sarcura, unveils an on-chip flow cytometer using integrated photonics. Fabricated on imec’s 200mm CMOS pilot line, the opto-fluidic chip features a pioneering material stack facilitating both cell illumination and capturing of scattered light through waveguide optics, and precise cell delivery to the detection points using microfluidic channels.
“Silicon photonics, as successfully demonstrated in this novel photonic chip, is the revolutionary and essential building block that merges single-cell detection capabilities with massive parallelization on a dramatically miniaturized footprint. This breakthrough opens new possibilities for addressing previously unsolved challenges in applications such as cell therapy manufacturing," states Daniela Buchmayr, CEO and Co-founder of Sarcura.
Niels Verellen, Scientific Director at imec, remarked, “We have demonstrated, for the first time, that a monolithically integrated biophotonic chip can be used to collect optical scattering signals that allow the discrimination of lymphocytes and monocytes from a patient’s blood sample, rivaling the performance of commercial cytometers. The main advantage lies in the potential for dense parallelization of multiple flow channels to boost the system throughput.” In a next phase, the compact, alignment-free design should enable billions of cells to be identified within a limited amount of time.
Crucially, the chip architecture seamlessly integrates with imec’s previously developed bubble jet cell sorting module, compatible with wafer-scale fabrication. Furthermore, the photonic components and layout can be tailored to suit specific applications. This proof-of-concept therefore marks a substantial leap towards cost-effective, scalable, and highly parallelized cell sorting platforms.
IMEC Belgium
3001 Leuven
Belgium